Comprehensive Car Insurance in Vietnam: Protecting Your Investment
Understand coverage types, compare voluntary vs. mandatory options, evaluate providers, and choose the right protection level for your budget.
In Vietnam, every car must carry TNDS (mandatory third-party liability) to drive legally. But TNDS
only covers damage or injury to others. To protect your own vehicle against accident damage, theft,
flood, fire, and more, you need voluntary comprehensive insurance. This guide explains what comprehensive
coverage includes, how it compares to TNDS, the differences between international and local insurers, and how to run a
practical cost–benefit analysis so you can insure smarter.
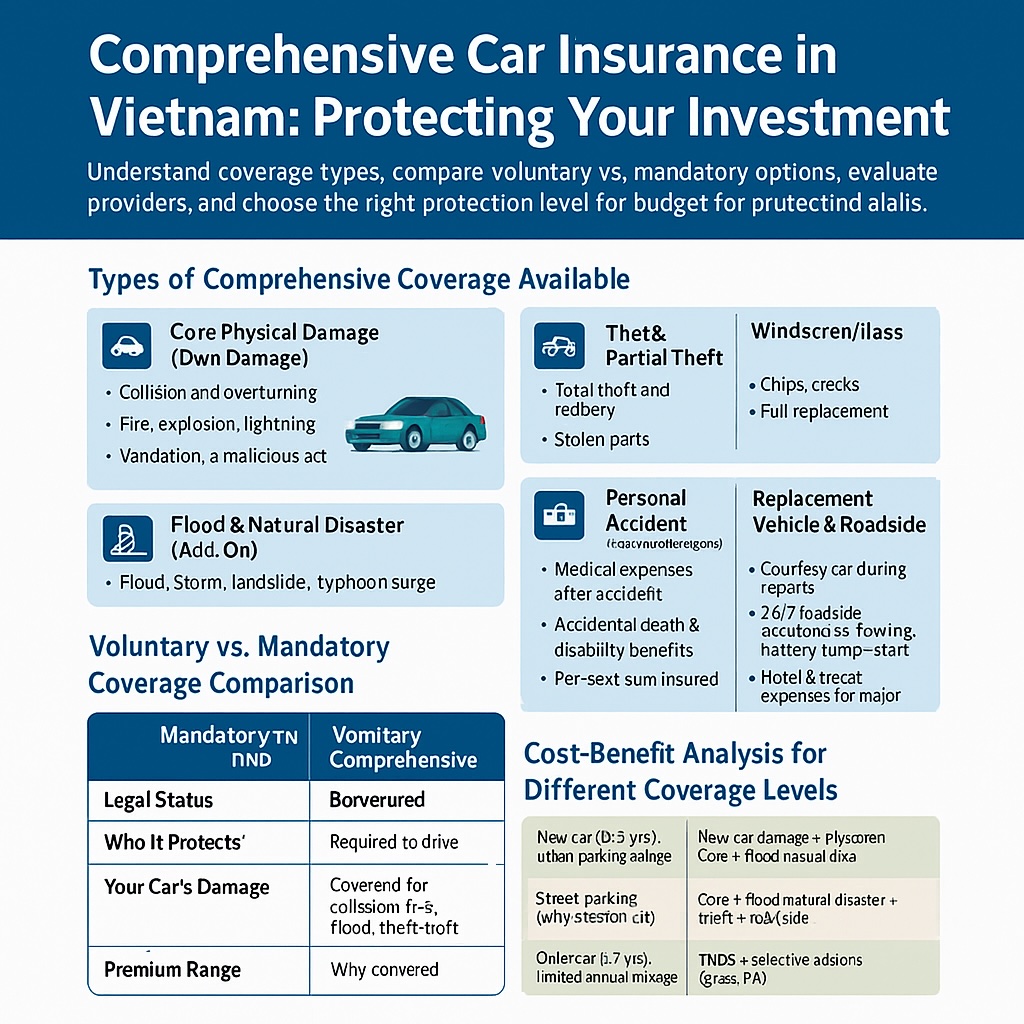
A. Types of Comprehensive Coverage Available
Comprehensive policies are modular. Start with core physical damage cover and add riders to match your risk profile.
1) Core Physical Damage (Own Damage)
- Collision and overturning (repairs or total loss payout)
- Fire, explosion, lightning
- Vandalism and malicious acts
- Towing after insured incident (limits apply)
2) Flood & Natural Disaster (Add-On)
- Flood, storm, landslide, typhoon surge
- Water ingress to engine & electronics (hydrolock often needs engine care rider)
- Recommended in rainy season and coastal cities
3) Theft & Partial Theft
- Total theft and robbery
- Stolen parts (mirrors, wheels) — often sub-limited
- Requires police report; anti-theft proof may reduce deductibles
4) Windscreen/Glass
- Chips, cracks, or full replacement
- Cashless repair at partner workshops
- Usually no impact on NCD if repaired (insurer-specific)
5) Personal Accident (Driver & Passengers)
- Medical expenses after accident
- Accidental death & disability benefits
- Per-seat sum insured; choose realistic limits
6) Replacement Vehicle & Roadside
- Courtesy car during repairs (daily caps)
- 24/7 roadside assistance, towing, battery jump-start
- Hotel & travel expenses for out-of-city breakdowns (optional)
Deductibles & NCD: Most comprehensive plans apply a deductible per claim. A clean year may earn
No-Claim Discount (NCD) at renewal; some add-ons preserve NCD for glass-only repairs.
B. Voluntary Comprehensive vs. Mandatory TNDS
Use this side-by-side table to see what each policy type does for you.
| Feature |
Mandatory TNDS |
Voluntary Comprehensive |
| Legal Status |
Required to drive on public roads |
Optional but highly recommended |
| Who It Protects |
Third parties (injury & property) |
Your own car + optional riders |
| Your Car’s Damage |
Not covered |
Covered for collision, fire, flood, theft (per policy) |
| Add-Ons |
Not applicable |
Glass, flood, theft, roadside, replacement car, PA |
| Premium Range |
Low (state-regulated) |
Medium to high (depends on car value, deductibles, add-ons) |
Bottom line: TNDS keeps you legal; comprehensive keeps your finances intact when your car is damaged.
Most owners combine both.
C. International vs. Local Insurance Providers
Vietnam’s market includes global brands and established local insurers. The best choice depends on service network,
claim experience, and how much English-language support you need.
International Providers – Typical Strengths
- English policy wording & expatriate-friendly service channels
- Cashless repair networks with OEM parts emphasis
- Clearer claims playbooks and digital apps
Consider if: you prefer English support, own a newer/upper-segment car, or travel between cities often.
Local Providers – Typical Strengths
- Broad provincial presence; familiarity with local repair shops
- Competitive premiums & flexible deductibles
- Fast on-site surveyors in major cities
Consider if: you want lower premiums and are comfortable with Vietnamese service channels.
Decision tip: Ask for cashless partner lists, paint and parts standards (OEM vs. aftermarket),
and average claim turnaround times in your city. Service quality can matter more than a small price gap.
D. Cost–Benefit Analysis: Picking the Right Coverage Level
Use these frameworks to align premiums with your real risk. Consider car value, parking, commute, and rainy-season exposure.
| Scenario |
Risk Profile |
Recommended Coverage |
Why |
| New car (0–3 yrs), urban parking garage |
Medium risk (minor collision, glass) |
Core damage + windscreen + PA; moderate deductible |
Keeps premiums reasonable while protecting expensive parts |
| Street parking, rainy-season city |
Higher flood & theft exposure |
Core + flood/natural disaster + theft + roadside |
Addresses the most likely high-cost events |
| Older car (>7 yrs), limited annual mileage |
Lower replacement value |
TNDS + selective add-ons (glass, PA); higher deductible |
Controls premium where full cover may not be cost-effective |
| Frequent intercity travel |
Accident & breakdown exposure |
Core + roadside + replacement vehicle + PA |
Minimizes downtime and out-of-pocket travel costs |
How to Tune Your Premium
- Deductible: Higher deductible → lower premium; ensure you can comfortably pay it.
- Sum insured: Based on market value; under-insuring reduces payout proportionally.
- Repair standard: OEM parts and dealer networks cost more but protect resale value.
- Driver/usage limits: Named drivers and mileage caps can lower cost if they match reality.
- NCD protection: Add-ons may preserve discounts after small claims.
Quick math example: If an annual comprehensive premium is 2.5% of car value and a typical collision
could cost 15–30% of value to repair, one covered incident in 4–6 years can “pay back” the premiums—especially when
flood/theft risk is material.
E. Buyer’s Checklist (Copy, Save, and Use)
- Confirm TNDS status and expiry date
- Choose comprehensive core + essential add-ons (flood, theft, glass, PA, roadside)
- Validate cashless partner workshops near your home/office
- Agree on deductible, parts standard, and maximum towing distance
- Store e-policy, hotline, and claim checklist in your phone & glove box
Want side-by-side quotes and expat-friendly claim support?
Compare comprehensive packages, riders, and deductibles in minutes.
Explore CarPlan24.com
Disclaimer: Information provided for general guidance in 2025. Policy terms, premiums, and claim procedures vary by insurer and province.
Always read your policy wording and confirm current requirements with your provider.